Thyroid Gland Disorders

The thyroid gland impacts the metabolic processes in the body through the hormones it releases. Thyroid disorders can range from a life-threatening condition such as cancer to a condition as harmless as a goiter. Usually, thyroid maladies are a result of abnormal secretion of thyroid hormones. If there are too many thyroid hormones secreted the condition is called hyperthyroidism while secretion of an inadequate amount of hormones is referred as hypothyroidism. Early diagnosis by an ENT doctor can help individuals to manage their thyroid symptoms well.
In Singapore, the ENT Clinic is among the best ENT practices to consider with state-of-the-art facilities following evidence-based medicine. It has some of Singapore’s best adult and paediatric ENT specialists, well versed with the latest diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. It is important to have an ENT consultation when one has a thyroid problem; serious complications can occur if left untreated.
Table of Contents
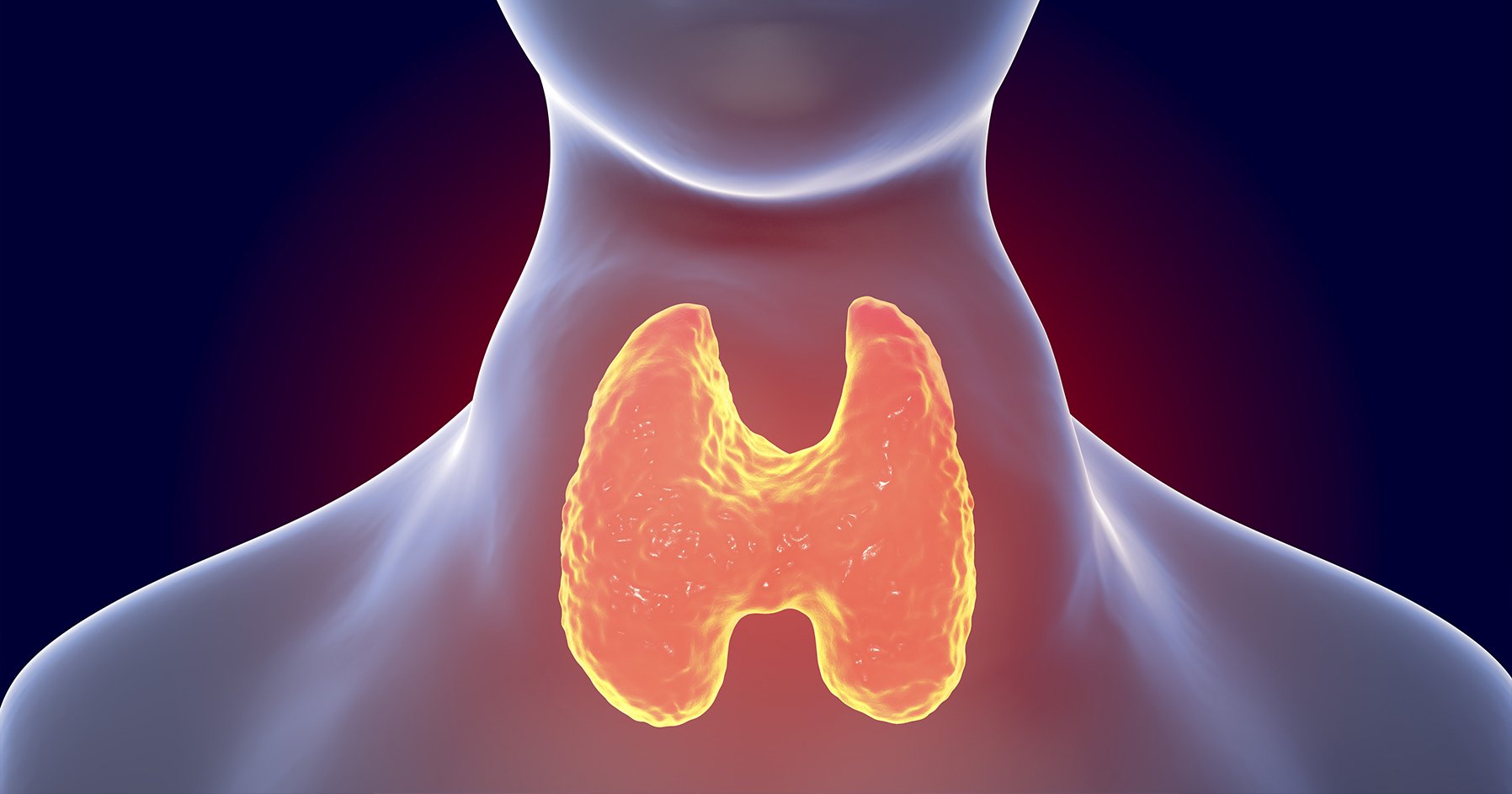
What Is The Thyroid Gland?
It is an endocrine gland present in the neck which secretes the two hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These hormones help normal metabolism. Imbalance in thyroid hormone secretion occurs more in women. The thyroid gland is present in front of the neck just below the Adam’s apple. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine hormones regulate the speed with which body cells work. When the balance between these two hormones go beyond the normal levels it leads to disorders.
What Is Hyperthyroidism And Its Impact?
Hyperthyroidism is having an overactive thyroid gland which produces too much thyroxine. This can accelerate the metabolism rate of the body. It can cause an irregular heart rate and weight loss. Individuals generally show bulging eyes and vision problems. Surgery may be needed to remove part of the thyroid gland to prevent over activeness. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include unexplained weight loss, rapid and irregular heartbeat, palpitations, tremors, sensitivity to heat, skin thinning and brittle hair. Older adults may have no signs or just subtle ones like fatigue even in ordinary activities.
What Is Hypothyroidism And Its Impact?
Hypothyroidism is having an underactive thyroid. Not enough hormones are secreted which causes one to have a sluggish metabolic system. This may not be very noticeable in early stages, but with time it can lead to obesity, heart disease and joint pain. Treatment is usually with synthetic thyroid hormones which are safe and effective. Some of the other common symptoms include constipation, dry skin, weight gain, increased sensitivity to cold, muscle weakness and high cholesterol levels. In addition, it could bring about impaired memory and an enlarged thyroid gland.
What Causes Thyroid Disorders?
Thyroid disorders may be caused due to many reasons. One of the most common causes is having an autoimmune thyroid disease, which is a self-destructive process where the immune system of the body attacks the thyroid cells considering it is like foreign cells. This can lead to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. It is also genetically linked and can be passed down. Some of the other causes include:
Thyroiditis: Inflammation in the thyroid gland. This condition can lower the number of thyroid hormones produced.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: This is an autoimmune disease where the body cells attack and damage the thyroid. It is an inherited condition.
Postpartum thyroiditis: A temporary condition which may be present in less than 10% of women after birth.
Deficiency in iodine: Deficiency in iodine can affect the hormone production of the thyroid gland.
Congenital defect of thyroid gland: One can be born with a thyroid gland which is not functioning well. Such a condition needs immediate intervention. If this condition is left untreated it can affect the physical and mental wellbeing of the child. Screening blood tests are generally done in the hospital.
Other conditions which can lead to hyperthyroidism are:
Graves disease: This condition brings about an overactive thyroid gland, which produces too much of hormones and it is also referred to as diffuse toxic goitre.
Nodules: The presence of overactive thyroid nodules can lead to a multi nodular goitre. It can be present singularly or in clusters.
Excessive iodine: When there is too much iodine in the thyroid, it makes excess hormones than it needs, leading to hyperthyroidism. Certain medications like amiodarone and cough syrups too have excess iodine.
What Are The Diagnosis Tests For Thyroid Gland Disorders?
Firstly, a physical examination is done by an otolaryngologist to check the neck for any enlargement or growths. It is a simple, painless test.
There are specific blood tests which are done to find if there is abnormal secretion of hormones. This includes:
Blood tests to check the levels of thyroid stimulating hormones. This is generally the first test done by an ENT doctor to check the thyroid hormone imbalance. Hypothyroidism is associated with elevated TSH levels. Other blood tests include, checking the thyroxine or T4 levels, checking of free T4 or free thyroxine levels. Blood tests for triiodothyronine too help to diagnose hyperthyroidism. Together with these tests, there maybe additional blood tests needed for diagnosis such as:
Thyroid antibodies: This helps to identify different autoimmune thyroid conditions such as microsomal antibodies, thyroglobulin antibodies and thyroid receptor antibodies.
Calcitonin: This helps to diagnose C-cell hyperplasia and medullary thyroid cancer
Thyroglobulin: It helps to diagnose thyroiditis and monitors treatment for thyroid cancers.
The other tests include imaging tests, such as getting a thyroid scan performed. The scan helps the ENT doctor to observe the thyroid if there are any changes in the size and shape as well as to see for the presence of nodules. Ultrasound scans may also be done.
What Are The Treatment Methods For Thyroid Gland Disorders?
The ENT doctor will try to bring the thyroid hormone levels to the expected range. High thyroid hormone levels can be controlled by using anti-thyroid drugs as well as radioactive iodine. Beta blockers can help to control symptoms. Thyroidectomy, which is surgery to remove the thyroid gland, helps to stop the creation of hormones. If the thyroid hormones are low, then thyroid replacement medications will be prescribed. These are synthetic drugs which can add thyroid hormones back to the body. Levothyroxine is a common drug used.
How Is Thyroid Removal Surgery Done?
The ENT specialist will determine if the thyroid has to be removed based on the severity of the condition. There are a few ways it is done, the doctor will determine if complete or partial removal is needed. Thyroidectomy is the name of the surgery performed to remove the thyroid gland. It is done with an incision on the front of the neck or by putting an incision in the armpit. The latter is the more modern approach as it is scarless since the incision is under the armpit.

 Depression Isn’t Just Sadness: A Psychiatrist Explains the Difference
Depression Isn’t Just Sadness: A Psychiatrist Explains the Difference  How Regular Acupuncture in London Can Support Fertility, Pregnancy, and Postpartum Recovery
How Regular Acupuncture in London Can Support Fertility, Pregnancy, and Postpartum Recovery  The Ultimate Guide to Cellular Health: From Methylene Blue to Shilajit
The Ultimate Guide to Cellular Health: From Methylene Blue to Shilajit  Your First Acupuncture for fertility session: What to Expect
Your First Acupuncture for fertility session: What to Expect  MTHFR Test: What You Need to Know Without the Medical Jargon
MTHFR Test: What You Need to Know Without the Medical Jargon  Experience the Power of WellHealthOrganic Laser Technology
Experience the Power of WellHealthOrganic Laser Technology  Criminal Defense Firm DCD LAW: A Client-Centered Approach to Protecting Rights
Criminal Defense Firm DCD LAW: A Client-Centered Approach to Protecting Rights  What Actually Happens During a 200-Hour Yoga Teacher Training
What Actually Happens During a 200-Hour Yoga Teacher Training  Why Every Chiropractor Needs Professional Liability Insurance: Lessons from the Clinic
Why Every Chiropractor Needs Professional Liability Insurance: Lessons from the Clinic