Everything You Need To Know About Botox Injections
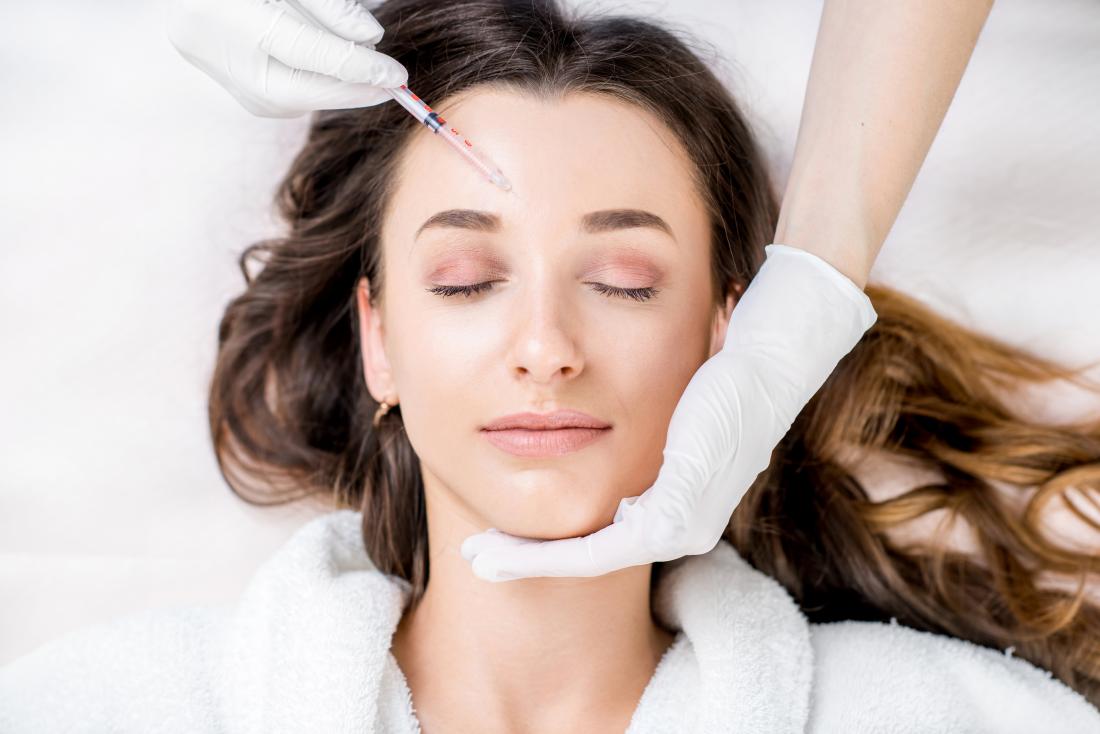
Following Botox administration, muscles become weak or paralyzed. A small dose of this substance can reduce skin wrinkles and treat certain medical conditions.
Botulinum toxin is produced by Clostridium botulinum bacteria. This is the substance used in botox. Similarly, botulism is caused by such toxins.
When used properly and in small amounts, Botox can help people despite the fact that it is a toxin. The product can be used to both address cosmetic and medical issues.
With botox Injections in Lincoln, wrinkles can be reduced as an aesthetic treatment. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved, it is used for treating eyelid spasms, excessive sweating, certain bladder problems, and migraines as well.
The study of Botox’s use, side effects, and other risks provides insight into how it works.
Table of Contents
How Can Botox Be Used?
Botox is made up of botulinum toxin, which is derived from the vitamin C. In the natural environment, botulinum bacteria occur in soil, lakes, forests, and the guts of mammals and fishes.
Botulinum is naturally present in the body. There is no harm done by botulinum spores and bacteria. In the presence of multiplication and transformation, problems arise. Toxins, such as botulinum toxin, are produced by bacteria at a certain point during their life cycle.
A botulinum toxin injection carries a high level of risk. One gram of the crystalline form of the toxin can kill 1 million people, and a few kilograms of it will kill every human on earth.
Botox has few side effects when used appropriately in a therapeutic context, according to a report by the American Osteopathic College of Dermatology.
Using very small quantities of Botulinum toxin, Botulinum toxin injections are made. The drug temporarily paralyzes muscles and can be used to treat a wide variety of muscle and nerve disorders.
Among the forms of botulinum toxin available commercially are:
- (Botox) Toxin A
- Dysport (Onabotulinumtoxina)
- The Botulinum Toxin A (Xeomin) is produced by Co Botulinum
- The myobloc toxin (rimabotulinumtoxinB)
- The Jeuveau botulinum toxin (Apra)
Even though Botox is a registered trademark that only one company owns, people often refer to all of these products collectively as “Botox.”.
How Does it Work?
The neurotoxin Botox is a neurotoxin. The goal of these substances is to disrupt nerve signals in the nervous system rather than stimulating muscle contractions. As a result, the drug causes a temporary paralysis of the muscles.
The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings signals the muscle to contract when nerves meet muscle cells. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on muscle cells to cause them to contract.
With Botox injections, the acetylcholine is prevented from being released, so the muscles cannot contract. Hence, it reduces stiffness of the muscles.
Cosmetics
It is most commonly used to treat wrinkles on the face by injecting Botox. A survey by the American Board of Cosmetic Surgery shows that Botox injections are the most commonly performed cosmetic surgery procedure in the United States. The number of Botox treatments exceeded 7 million in 2016.
Medicinal Purposes
Botox is one of the most common treatments for disorders of the neuromuscular system. Besides being approved for these uses, Botox has these other uses as well. A person must be 18 years of age or older to receive an approval, unless otherwise stated:
- Those who experience upper limb spasticity over the age of 2
- Over 12 year olds with strabismus, also called crossed eyes
- Sweating excessively under the arms, also known as hyperhidrosis
- When a migraine headache lasts longer than four hours for at least 15 days in a month, preventive medication should be considered
- In the case of overactive bladders caused by neurological conditions, anticholinergic medications do not reduce symptoms
- An eyelid spasm caused by dystonia is called blepharospasm
- Dystonia of the neck and head is caused by this ailment
In Addition, Botox injections Can be Used Unapproved for the Following Purposes:
- Angiopathy
- An excessive amount of saliva is produced due to sialorrheaTrusted Source
- Allergies
- Dyshidrotic eczema on the hands and feet
- A dysfunction of the anal canal leads to anismus
- Skeletal diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis
- Discomfort in the vaginal area, pain in the vaginal area, or a burning sensation in the vaginal area
- Raynaud’s syndrome affects the circulatory system
- The difficulty of swallowing is caused by achalasia


 Finding the Best Teen Mental Health Facility in Phoenix
Finding the Best Teen Mental Health Facility in Phoenix  Unleashing Your Ultimate Performance: How Dr. Sue’s Sport Hypnotherapy Transforms the Game
Unleashing Your Ultimate Performance: How Dr. Sue’s Sport Hypnotherapy Transforms the Game  Get Help for Your Teen: Understanding the Importance of Teen Mental Health Therapy
Get Help for Your Teen: Understanding the Importance of Teen Mental Health Therapy  Semaglutide Pills for Diabetic Patients and its role in Weight Management
Semaglutide Pills for Diabetic Patients and its role in Weight Management  How and When Must Drug Companies Participate in the 340B Program?
How and When Must Drug Companies Participate in the 340B Program?  What You Need to Know About Bacterial Infections: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
What You Need to Know About Bacterial Infections: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment  Tea Leoni Tim Daly Split – Are They Really Breaking Up? Full Story
Tea Leoni Tim Daly Split – Are They Really Breaking Up? Full Story  Tim Daly and Tea Leoni – Who Are They? Full Bio & Career
Tim Daly and Tea Leoni – Who Are They? Full Bio & Career  Breaking: Software TGD170.FDM.97 New Release Out Now!
Breaking: Software TGD170.FDM.97 New Release Out Now!  TGD170.FDM.97 New Release – What’s Inside the Latest Update?
TGD170.FDM.97 New Release – What’s Inside the Latest Update?